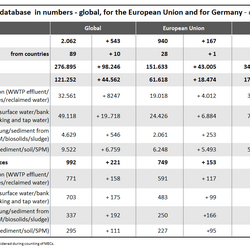
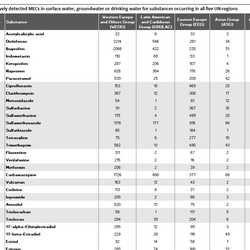
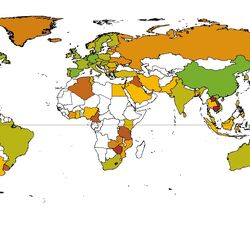
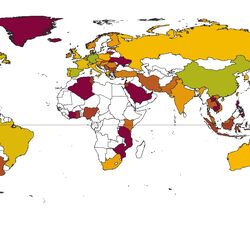
For the database 2,062 publications were comprehensively reviewed and analysed. Environmental concentrations of human and veterinary pharmaceutical residues could be collected for 61 matrices. Most pharmaceutical residues were found in surface water, groundwater, tap/drinking water as well as in soil and sediment.
The data were transferred from the publications, reports and other data sources into the database (MEC database). The database is available for download as Microsoft Excel© or as Microsoft Access© file. Each database entry comprises 33 fields, including amongst others the name of the pharmaceutical substance, its CAS number, the environmental matrix the substance was measured in, geographical location, sampling period, number of measurements, measured concentration in original and standardised units, detection limit of the analytical method employed, pollution source (if stated in publication), literature citation, publication language and type, and quality flag.
All references used were compiled in an Endnote© literature database. For transparency and to allow for better working with the MEC database please download here the literature database as travelling library and in other formats in a zip-file.
Since 2021 the PHARMS-UBA database can be accessed in the IPCHEM Portal.
A brief instruction how to access the PHARMS-UBA database is available here.