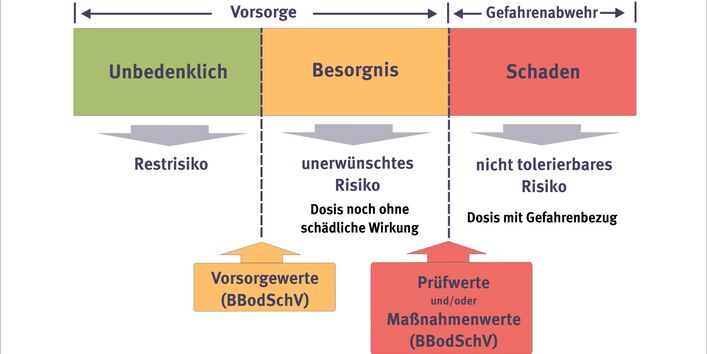
Limit values provide the answer to this question. They are derived using scientific (e.g. ecotoxicological or human-toxicological) methods. Important requirements for the analysis and assessment of pollutants in soil are laid down in the Federal Soil Protection and Contaminated Sites Ordinance (BBodSchV). The Ordinance contains detailed rules for sampling, sample preparation and chemical analysis as well as binding assessment standards. In addition to generally applicable precautionary values, the latter also include trigger and action values for specific pathways and uses.
Precautionary values differentiated by soil type exist for the metals lead, cadmium, chromium, copper, nickel, mercury and zinc and for the organic substances PCB6, benzo(a)pyrene and PAH16. Precautionary values are established on the basis of ecotoxicological effect thresholds and compared with rural background concentrations. They contain a safety margin in regard to the hazard-based trigger values. Where precautionary values are exceeded, the additional input of pollutants via all pathways must be limited to a maximum permissible load. There is concern that adverse effects may occur.
The precautionary values are applied, for example, where materials (mainly soil material, sewage sludge, biowaste) are applied onto or introduced into the soil as well as in the permitting of new industrial installations. They can also be used as targets for the cleanup of contaminated soil. To prevent an accumulation of pollutants from agricultural use, the soil protection requirements for the application of sewage sludge (Sewage Sludge Ordinance, AbfKlärV), liquid manure and fertilizers must be updated. Advising on needs-based use of fertilizers (Fertilisation Act, DüngG) and pesticides (Plant Protection Act, PflSchG) is being stepped up and financial incentives are being created with a view to minimizing harmful effects.
Additionally, the urgency and effectiveness of measures to reduce substance inputs can be evaluated throughout Germany by means of “critical loads”. Critical loads are area-related thresholds for pollutant input and take land use into account. Where critical loads are complied with, significant harmful effects on the ecosystem concerned are not expected to occur according to present knowledge.